Sub-Sahara Africa!
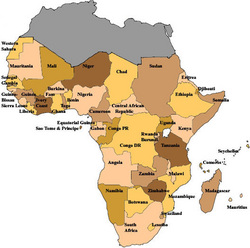
The Sub-Sahara Africa region is made up of 40 different countries.
These countries consist of:
Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, Swaziland, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
These countries consist of:
Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, Somalia, South Africa, Swaziland, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
Physical Features:
Geologists usually place Africa at the center of the ancient super continent Pangaea.
The Arabian Plate is one of the main features in Sub-Sahara Africa. The Arabian Plate has now drifted away from Africa and drifted north east leaving the Red Sea, which separates Africa and Asia.
The Great Rift Valley is another feature of Africa. The Great Rift Valley is another series of developing rifts that curve inland from the Red Sea and extends more than 2000 miles south to Mozambique, near the east coast.
Another distinctive feature of this region in Africa is its Escarpments or long cliffs that are around the rim of the continent and the long uniform coastlines that have a few natural harbors.
The surface of the continent of Africa can be looked upon as a raised platform, or plateau, bordered by a fairly narrow and uniformed coastal lowlands as well as covered by an ancient mantle of rock in various staged of weathering. The platform then slopes downward to the north. The Southeastern third of the continent is an upland region with several high peaks, whereas the northwestern two-thirds of the continent consists of lower lying landscapes, interrupted only here and there by uplands and mountains. Because of these mountains and various landforms here Africa has obstructed transport and hindered connections to the outside world.
The Arabian Plate is one of the main features in Sub-Sahara Africa. The Arabian Plate has now drifted away from Africa and drifted north east leaving the Red Sea, which separates Africa and Asia.
The Great Rift Valley is another feature of Africa. The Great Rift Valley is another series of developing rifts that curve inland from the Red Sea and extends more than 2000 miles south to Mozambique, near the east coast.
Another distinctive feature of this region in Africa is its Escarpments or long cliffs that are around the rim of the continent and the long uniform coastlines that have a few natural harbors.
The surface of the continent of Africa can be looked upon as a raised platform, or plateau, bordered by a fairly narrow and uniformed coastal lowlands as well as covered by an ancient mantle of rock in various staged of weathering. The platform then slopes downward to the north. The Southeastern third of the continent is an upland region with several high peaks, whereas the northwestern two-thirds of the continent consists of lower lying landscapes, interrupted only here and there by uplands and mountains. Because of these mountains and various landforms here Africa has obstructed transport and hindered connections to the outside world.
Climates:
Most of sub-Saharan Africa has a tropical climate. This is because seventy percent of the continent lies between the tropic of Cancer and the tropic of Capricorn. Temperatures average around 64 degrees year round everywhere except at the more temperate southern tip of the continent and in cooler upland zones. Climate in Africa can differ more by the amount of rainfall it receives then it differs by temperature.
Intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ): a band of atmospheric currents that circles the globe roughly around the equator. Warm winds converge from both north and south and push against each other causing the air to rise, cool, and release moisture in the form of rain. The rainfall produces here is the most abundant in central and western Africa near the equator.
The Horn of Africa is one of the driest parts of the continent. Along the coast of the Nambi Desert moist air from the Atlantic is blocked from moving over the desert by cold air above the northward flowing Benguela Current. The Benguela Current is chilled by its passage past Antarctica.
Because of the climate in Africa there is a number of challenges to human habitation. Parasites and insects that breed prolifically in warm, wet climates cause and spread debilitating diseases such as river blindness, and malaria. In the drier and tropical climates, water for drinking, farming, and raising animals is often in short supply. There is some evidence that Africa has experienced repeated climate changes over the last 20,000 years. Scientists think that many of the changes occurring over there today are at least partly the result of global warming caused by the rising levels of greenhouse gases produced in the industrialized parts of the world.
Intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ): a band of atmospheric currents that circles the globe roughly around the equator. Warm winds converge from both north and south and push against each other causing the air to rise, cool, and release moisture in the form of rain. The rainfall produces here is the most abundant in central and western Africa near the equator.
The Horn of Africa is one of the driest parts of the continent. Along the coast of the Nambi Desert moist air from the Atlantic is blocked from moving over the desert by cold air above the northward flowing Benguela Current. The Benguela Current is chilled by its passage past Antarctica.
Because of the climate in Africa there is a number of challenges to human habitation. Parasites and insects that breed prolifically in warm, wet climates cause and spread debilitating diseases such as river blindness, and malaria. In the drier and tropical climates, water for drinking, farming, and raising animals is often in short supply. There is some evidence that Africa has experienced repeated climate changes over the last 20,000 years. Scientists think that many of the changes occurring over there today are at least partly the result of global warming caused by the rising levels of greenhouse gases produced in the industrialized parts of the world.
Resources:

Mixed Agriculture: grow crops and raise livestock.
Cash Crops include: Peanuts, cacao beans, rice or coffee.
Herding, Pastoralism: practiced in the Savannas, on desert margins, or in the mixture of grass and shrubs called open bush. Herders use milk, meat, and hides, and trade those usually for things like grain, vegetables, and other necessities with other settled farmers.
Exports of Raw Materials: Bauxite, cocoa, coffee, copper products, diamonds, iron ore, livestock/animals, nuts, Oil/natural gas, petroleum products, sugar, tobacco, uranium, vanilla.
Cash Crops include: Peanuts, cacao beans, rice or coffee.
Herding, Pastoralism: practiced in the Savannas, on desert margins, or in the mixture of grass and shrubs called open bush. Herders use milk, meat, and hides, and trade those usually for things like grain, vegetables, and other necessities with other settled farmers.
Exports of Raw Materials: Bauxite, cocoa, coffee, copper products, diamonds, iron ore, livestock/animals, nuts, Oil/natural gas, petroleum products, sugar, tobacco, uranium, vanilla.
Religions:
1. Indigenous Belief systems: Animism. Has some of the most ancient heritage of any religion on earth and are found in every part of Africa. According to these beliefs, all entities- plants, animals, and specific landscape features- are part of a whole that includes the entire environment. Traditional beliefs and rituals seek to bring the vast host of departed ancestors into contact with people now alive, who in turn, are the connecting links in a timeless spiritual community that stretches into the future.
2. Islam and Christianity:
a. Islam began to extend south of the Sahara, especially into East Africa.
b. Christianity extended more into the south of Africa.
2. Islam and Christianity:
a. Islam began to extend south of the Sahara, especially into East Africa.
b. Christianity extended more into the south of Africa.
Environmental Issues:
Desertification: which conditions are arid and spread to areas that were previously moist.
Dry Forests: those forest that loose their leaves during extended dry seasons; they are being destroyed faster than rain forests because they are closer to developments, which are in greater need of their resources.
Wildlife and National Parks: The parks are trying to save many of the animals in Africa, which are referred to as “bush meat” because most of the people living in villages use these animals as their greater source and sometime their only source of protein. Some animals are being hunted to almost extinction. Some natural wildlife animals are being hunted also to protect livestock, like the cheetahs, which sneak into some farmer’s properties and steal their livestock’s.
Dry Forests: those forest that loose their leaves during extended dry seasons; they are being destroyed faster than rain forests because they are closer to developments, which are in greater need of their resources.
Wildlife and National Parks: The parks are trying to save many of the animals in Africa, which are referred to as “bush meat” because most of the people living in villages use these animals as their greater source and sometime their only source of protein. Some animals are being hunted to almost extinction. Some natural wildlife animals are being hunted also to protect livestock, like the cheetahs, which sneak into some farmer’s properties and steal their livestock’s.
Population Patterns:
The population in Africa is distributed unevenly, but generally sparsely over the continent. Only a few places here in Africa have the densities that are widely spread in Europe, India, and China. There are serious population problems in Africa. Some countries have pockets of very high density, but have not developed existing resources to support their people.
The Carrying Capacity: the maximum number of people it can support sustainably with food, water, and other essential resources. Carrying capacities in Africa vary widely across the huge continent, and the factors that limit carrying capacity also can vary from the place to place. The African populations on the other hand are growing faster than any others on earth. In less than fifty years, the population of the Sub-Saharan Africa more than tripled getting to an estimated 657 million people in 2000.
The Carrying Capacity: the maximum number of people it can support sustainably with food, water, and other essential resources. Carrying capacities in Africa vary widely across the huge continent, and the factors that limit carrying capacity also can vary from the place to place. The African populations on the other hand are growing faster than any others on earth. In less than fifty years, the population of the Sub-Saharan Africa more than tripled getting to an estimated 657 million people in 2000.
Technology:

A generation of entrepreneurs in Africa is but merely put down by Africa’s past problems, but driven by its potential in human and natural resources. They are well educated and familiar with global communication. Here they also desire to find similar opportunities in their own countries and have established businesses in a variety of areas.
Africa online is now the continents largest internet source. It was founded by three young Kenyan's who returned from the United States after graduating from MIT, Harvard, and Princeton.
Africa online is now the continents largest internet source. It was founded by three young Kenyan's who returned from the United States after graduating from MIT, Harvard, and Princeton.
Zimbabwe:
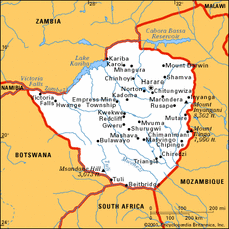
Once though of as having great promise, has become a worrisome failed state because of ill conceived development strategies and bad gobernance. But the main cause for worry in the region is the HIV-AIDS epidemic, which by 2005 threatened 20-40 percent of more of the adult popultation in every country in Southern Africa. This is a land of savannas, and open woodlands. The population density is low here. There is rich deposits of diamonds, gold, chrome, copper, uranuim, and coal found here as well as the whole southern part of Africa. Zimbabwe is still overwhelmingly rural. Agriculture and related food processing industries form an important part of their economies and their exports. Over the last two decades though, agriculture production has increasingly fallen. The economy here remains focused on extractive industries like commercial agricluture and mining. This is over 40 percent of the countries exports.
References:
Sub Saharan Africa Map from: http://www.nric.net/images/afr.jpg
Photo of the crops in africa from: http://www.farmafrica.org.uk/images/tanzania/TZ_Schools.JPG
Religion in Africa from: http://img.search.com/thumb/b/bc/Priestess.png/313px-Priestess.png
technology picture from: http://www.renewablepowernews.com/wp-content/uploads/img.jpeg
Zimbabwe map from: http://www.merriam-webster.com/maps/images/maps/zimbabwe_map.gif
Pulsipher, L.M., and Pulsipher, A. (2008). World Regional Geography: Global Patterns, Local Lives (4th ed.) Pages 353-411. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.
Photo of the crops in africa from: http://www.farmafrica.org.uk/images/tanzania/TZ_Schools.JPG
Religion in Africa from: http://img.search.com/thumb/b/bc/Priestess.png/313px-Priestess.png
technology picture from: http://www.renewablepowernews.com/wp-content/uploads/img.jpeg
Zimbabwe map from: http://www.merriam-webster.com/maps/images/maps/zimbabwe_map.gif
Pulsipher, L.M., and Pulsipher, A. (2008). World Regional Geography: Global Patterns, Local Lives (4th ed.) Pages 353-411. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company.

